Labs
Students will learn how to research and design engineering products through group and individual projects using various CAD software tools.
Featured Equipment:
- Siemens NX CAD and FEA software
- Engineering books and medical journals
- Anatomical models
- Basic measurement equipment
Here, students will have access to 3D printers that use metals, advanced polymers and composite materials.
Featured Equipment:
- Markforged Metal X and X7 3D printers
- EOS P 110 3D printer
Markforged X7 3D Printer
Students use this machine to fabricate industrial-grade parts or rapid prototyping from a full range of composite materials (carbon-fiber and others) in a process called continuous fiber reinforcement (CFR).
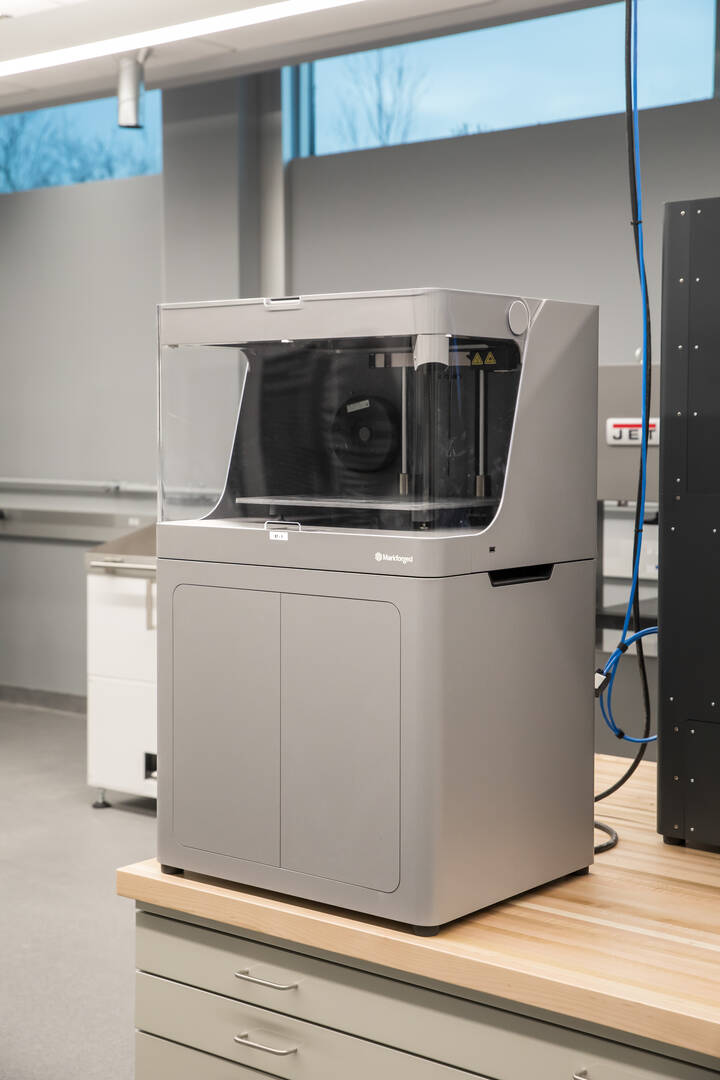

Markforged Metal X 3D Printer
Students use this machine to fabricate complex metal parts from a wide range of metals—including stainless steels, titanium and copper. The technology is called fused filament fabrication (FFF) where metal powder, bound in plastic, is printed a layer at a time into the shape of the part.

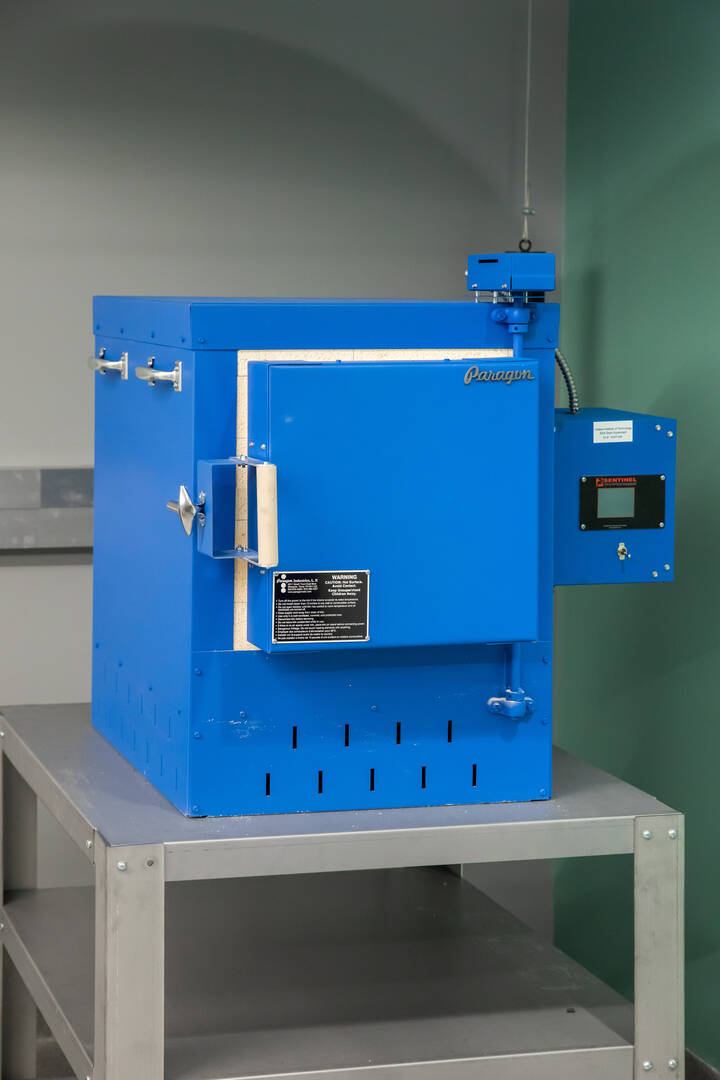
Kiln
Students use this kiln to post-treat parts printed by the EOS M 290 3D metal printer (located in the Thermal Sciences Lab). By subjecting the parts to the kiln’s intense heat—a process called stress relief—the parts become less prone to distortion.

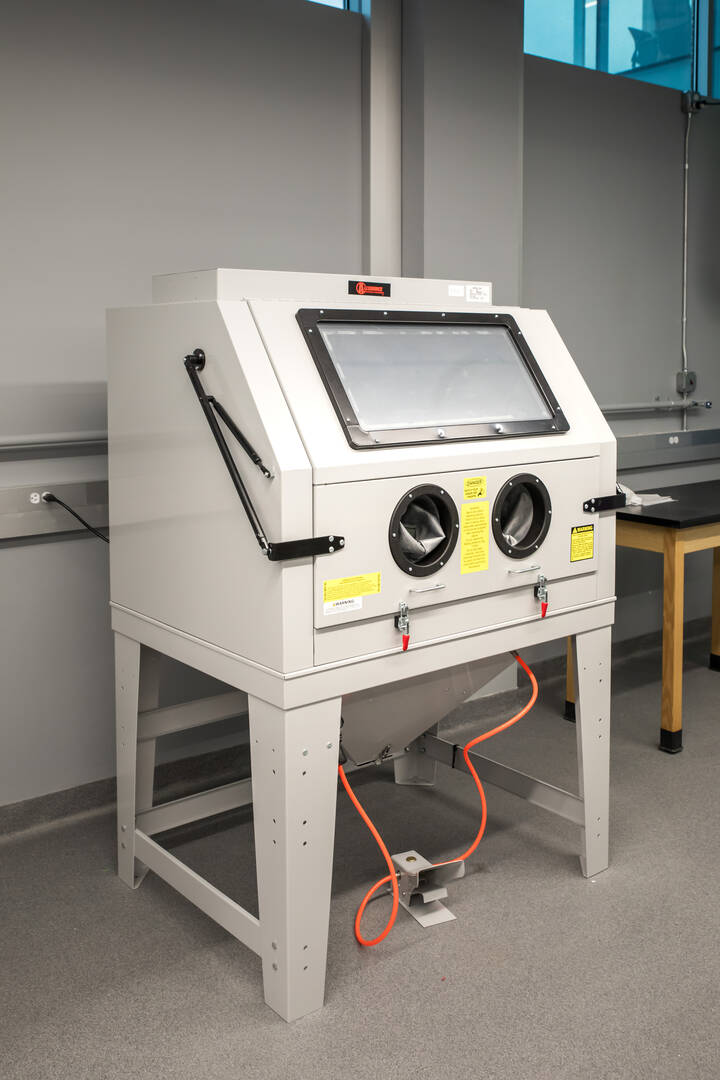
Abrasive-Blast Cabinet
Students use this cabinet to post-treat parts printed by the EOS M 290 3D metal printer (located in the Thermal Sciences Lab). Abrasive blasting removes unwanted support material from 3D prints. A process called shot peening smooths surfaces and blends in striation lines generated during 3D printing, which strengthens the part.

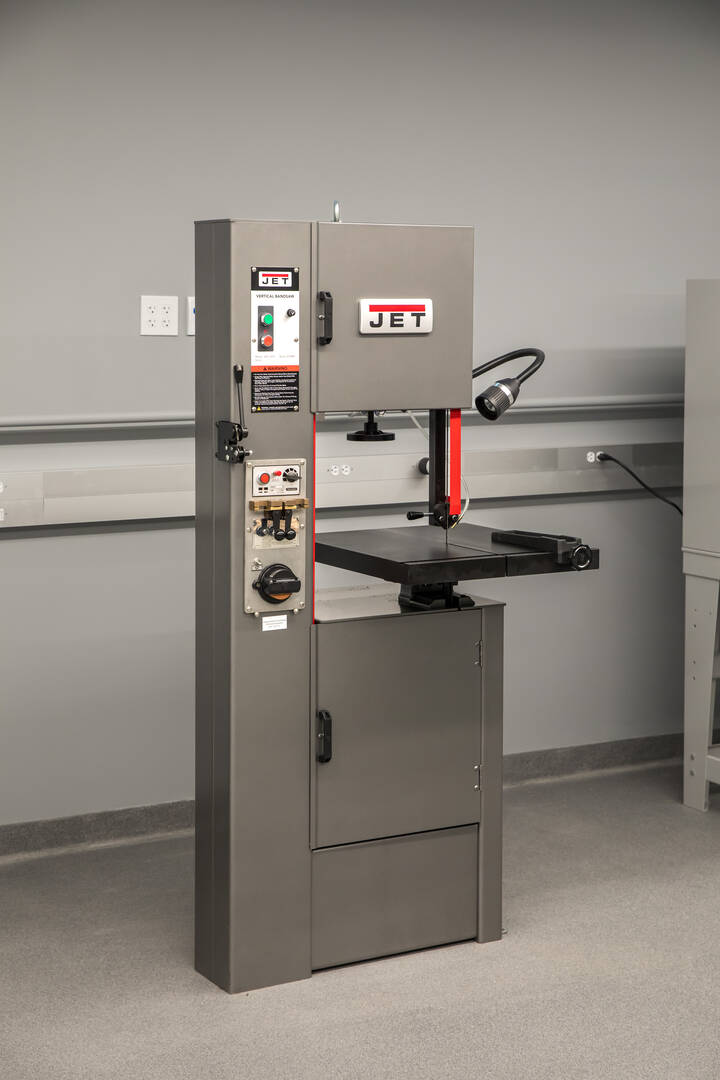
Band Saw
Students use this band saw to post-treat parts printed by the EOS M 290 3D metal printer (located in the Thermal Sciences Lab). The saw is used to remove the printed part from the build plate.

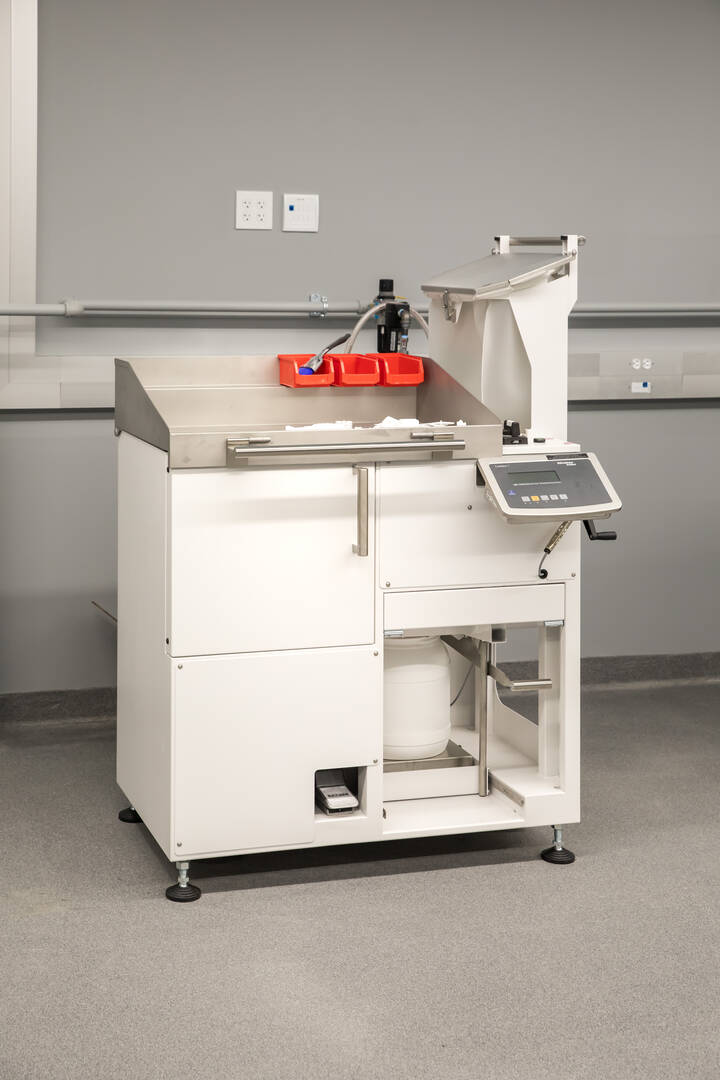
Post-Processing Station
Students use this post-processing station, primarily to remove excess material from their polymer 3D-printed parts.

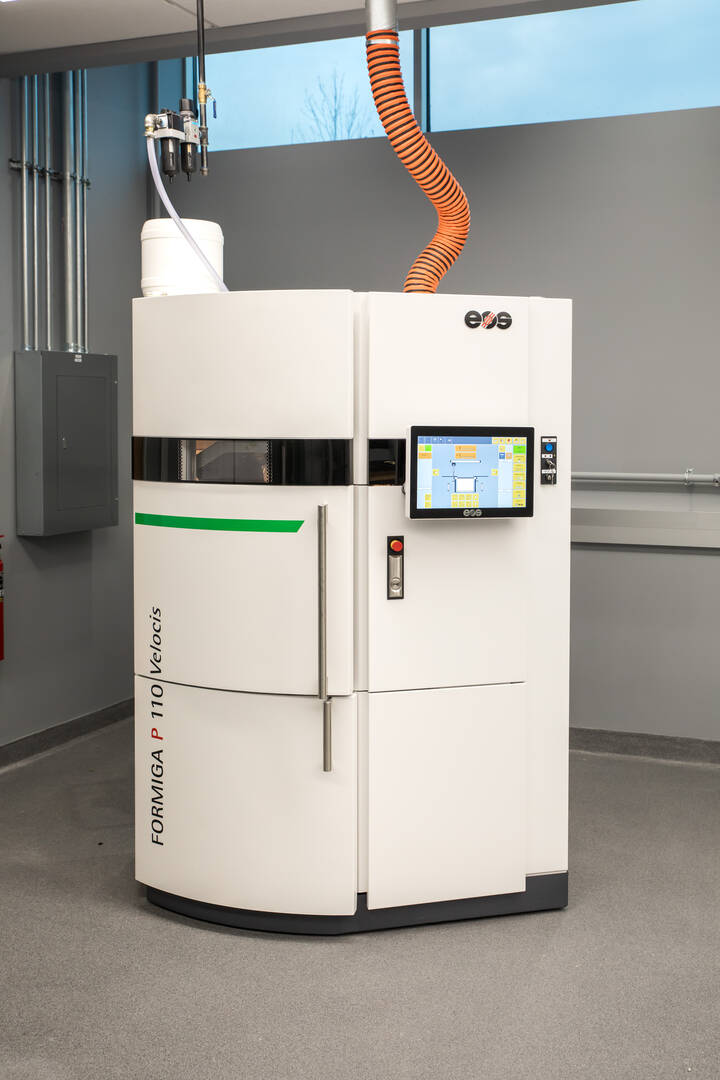
EOS FORMIGA P 110 Velocis 3D Printer
Students use this machine to fabricate industrial-grade parts from a wide array of highly developed polymer materials for additive manufacturing and rapid prototyping.

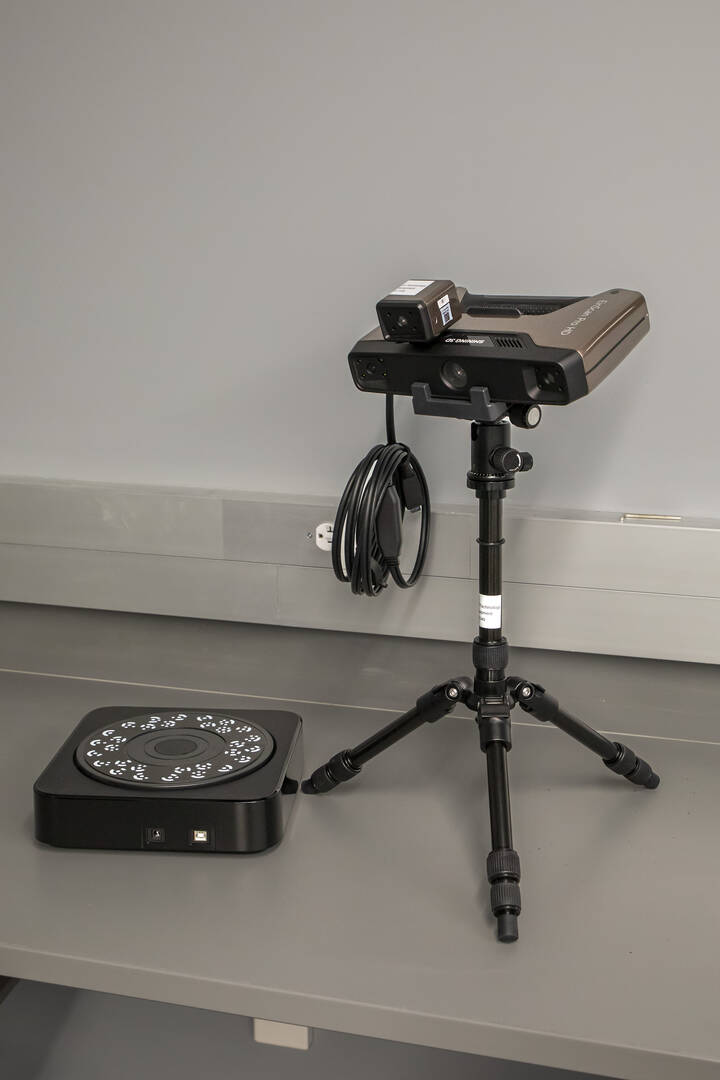
SHINING 3D EinScan Pro HD Scanner
Students use this equipment to capture accurate, high-resolution scans of 3D objects, which enables the creation of digital 3D models.

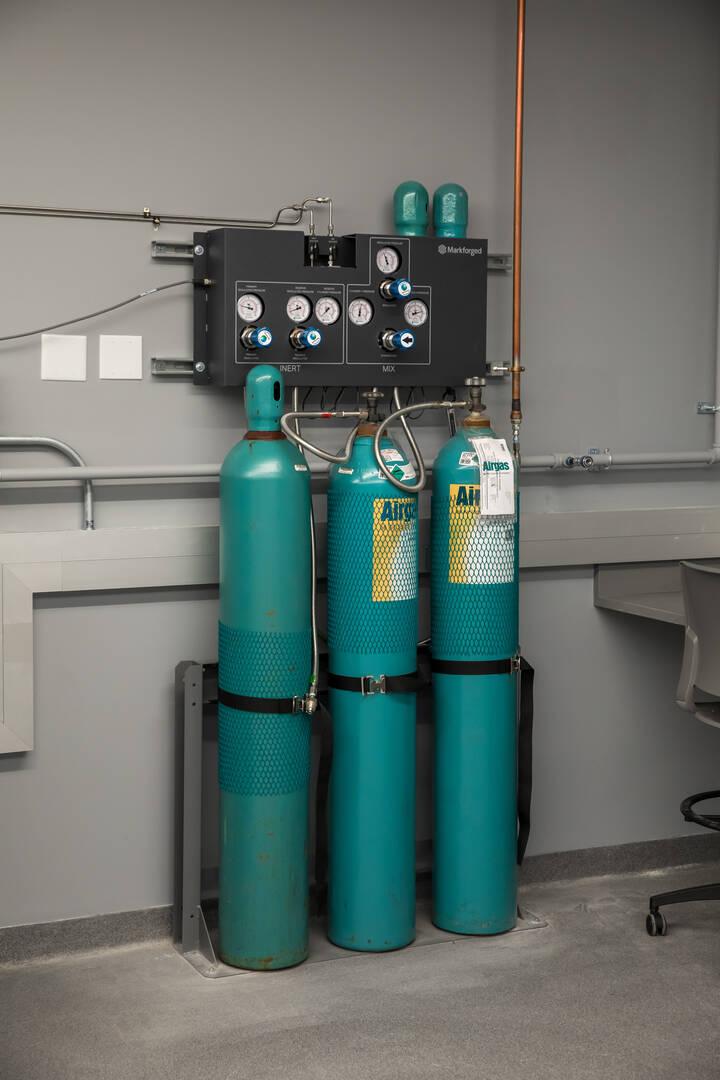
Argon Gas Station
Argon gas is used in the controlled atmosphere of the sinter furnace to prevent oxidation and to give printed parts a bright surface finish.

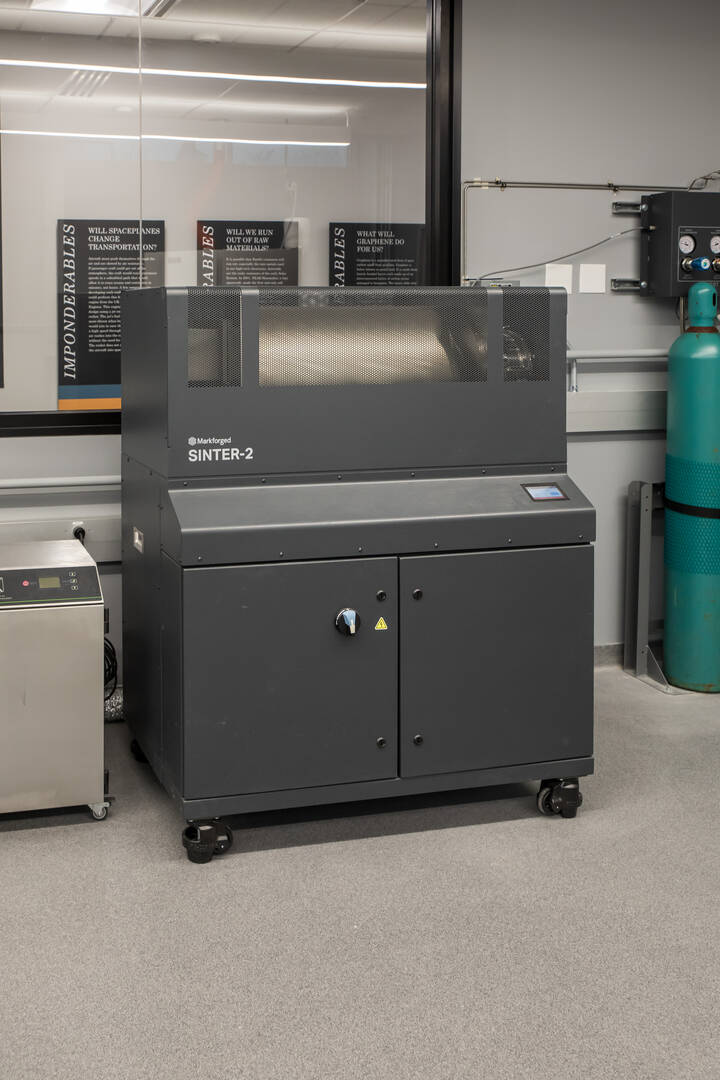
Markforged Sinter Furnace 2
Students use this furnace to post-treat parts printed by the Markforged Metal X 3D printer. In the controlled atmosphere of this furnace, raw parts undergo a process called sintering. The parts are subjected to intense heat which bonds together the metallic particles of the parts and maximizes their strength.

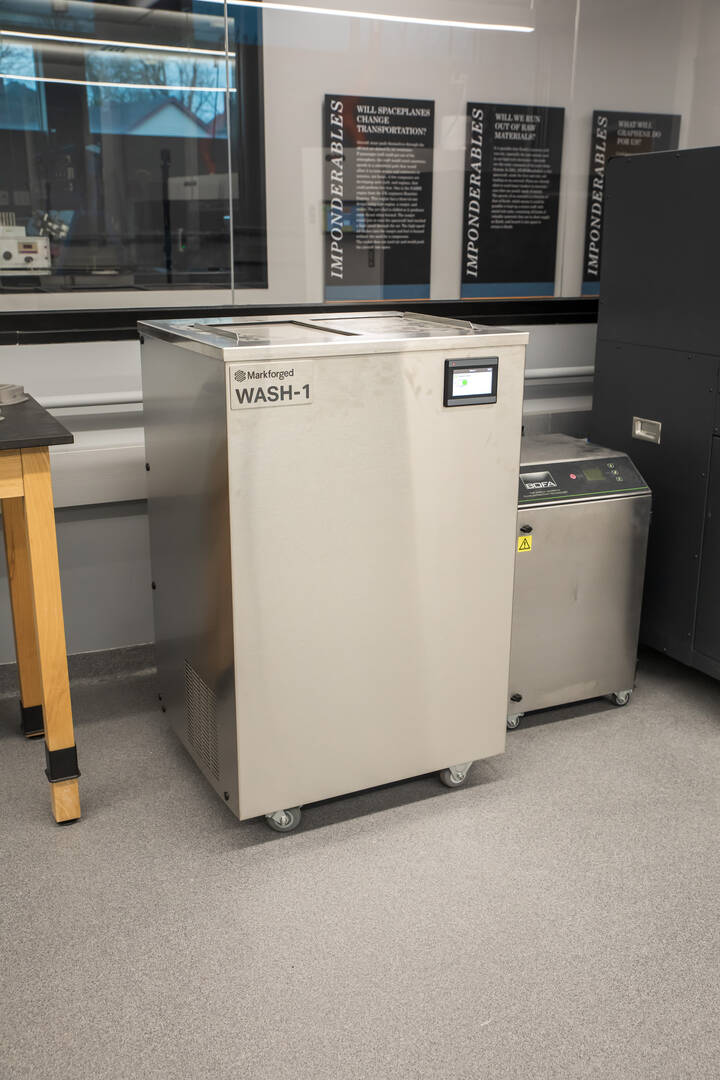
Markforged Wash-1 Washing Station
Students use this machine to post-treat Markforged Metal X 3D-printed parts to remove the metal binding matrix.

Here, students will apply advanced spectroscopy, chemical fractionation and computed analyses to extend organic synthesis work that is part of their two-semester series in organic chemistry. They will also be able to analyze compounds elicited from screens for novel antibiotics in collaborating courses. This lab is located in the Zollner Engineering Center Room Z212.
Located in the Zollner Engineering Center Room Z014, students will learn anatomy with an array of hands-on contemporary teaching tools, including cadavers. Students will also use this lab for developing and validating medical device designs and for the creation of their senior capstone projects.
Featured Equipment:
- Anatomage Table Virtual Cadavers
- Medical models
- Large-bone and small-bone battery-powered surgical equipment
- General surgical instrument sets
- Orthopedic surgery-specific instrument sets and implants
- Ultrasound machine
- Full-body human specimens
Part of Indiana Tech’s Center for Cybersecurity, this lab provides students with experience on a variety of security related topics like security information and event management (SIEM) system, vulnerability testing, cyber and CTF competitions, incident handling and building cybersecurity labs for ethical hacking.
Featured Equipment:
- Netlab host and management servers
- Netlab virtual software
- Dell & Lenovo servers
Students will get hands-on experience running this data center, which will also house a fully functional network and labs. Here, professors will be able to customize virtual environments to test their students’ knowledge and skills.
The center will feature a VMware-hosted environment, an enhanced digital forensics rack, room for more networking engineering devices, a wireless network and isolated networks for competitions and ethical hacking.
Part of Indiana Tech’s Center for Cybersecurity, this space is equipped with Forensic Recovery of Evidence (FRED) workstations, which give students the ability to perform authentic digital forensic analyses on simulated investigation scenarios.
Featured Equipment:
- FRED workstation
- FREDC server
- Digital forensic analysis softwares FTK and Autopsy
Students will learn by using oscilloscopes, function generators, DC power supplies, and desktop computers. Electronic components and IC of different types, as well as mutimeters, are also available.
Electrical Machines/Transformers and Control Lab
This lab is equipped with various types of state-of-the-art, computer-interfaced AC and DC motors, and single- and three-phase transformers. Using a servo drive and braking system, it is possible to easily simulate the performance of various motors (e.g., fans, pumps, compressors, flywheels) under different industrial loads.
Programable Logic Controllers Lab (PLC)
This lab is equipped with three Amatrol trainers, which are composed of an Allen-Bradley AB5300 L16 processor, a fault insertion system, and a PanelView Plus compact HMI panel. The trainer has the distinct feature of mimicking practical industrial temperature control application, variable speed drive application, reversing contractor application and stepper motor control application.
LabVIEW and Data Acquisition (DAQ) Lab
This lab is equipped with 10 LabVIEW licenses on 10 different computers, in addition to six LabJack U3-LV DAQ systems. This lab will provide students hands-on-experience in using industry-standard software that is used in 35,000 companies around the world.
PCB Rapid Prototyping Lab with LPKF Circuit Board Milling Machine
Equipped with an S103 LPKF Laser & Electronics benchtop prototyping system, this lab gives students experience in designing electronic circuits and creating printed circuit board (PCB) schematics.
Students will have access to machining and welding equipment, tools and other resources to get hands-on experience with manufacturing processes and fabrication. Here, all engineering students will be able to build projects that are required as part of their coursework.
Featured Equipment:
- TIG, MIG and oxyacetylene welding equipment
- CNC plasma cutter table
- Milling machines (CNC and manual)
- Lathes (CNC and manual)
- Parts washer
- Belt and disk sander
- Drill press
- Sheet metal shear
- Miscellaneous cutting, hand and power tools
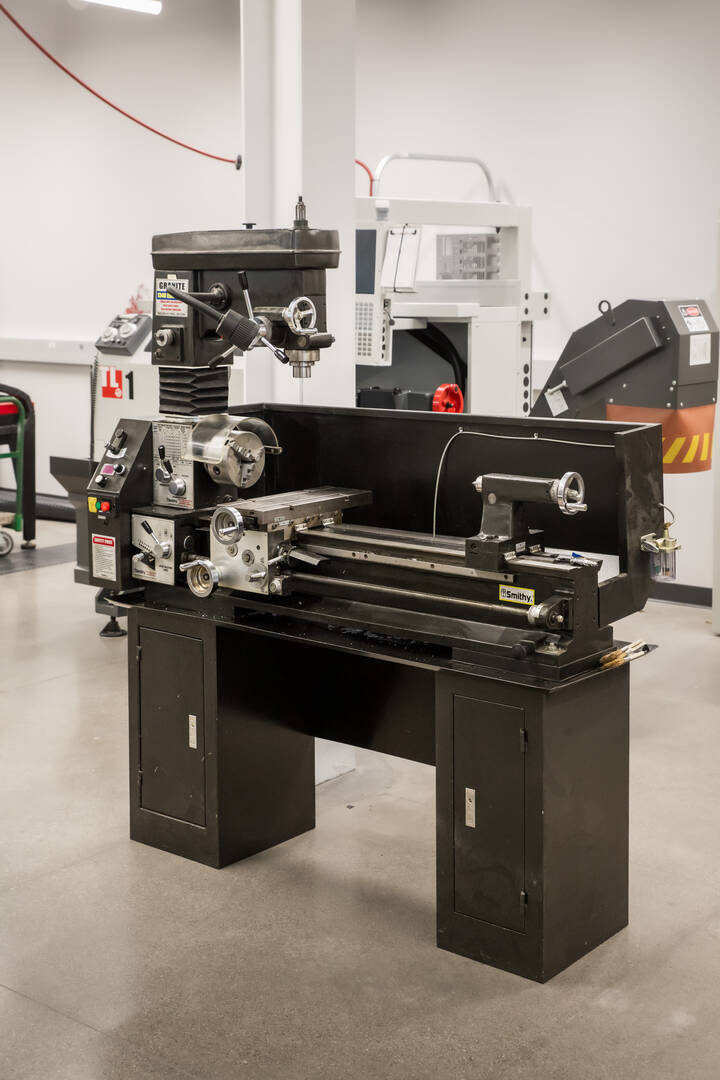
Smithy Lathe/Mill Combo
This machine contains lathing and milling capabilities that give students the capability to create products that would require four axes of movement. A bolt, for example, can be made on a regular lathe to produce the head diameter, the shaft and the threads. However, a regular lathe can’t make the cuts needed to make it a hex bolt. This machine can make the eight straight cuts without the need to set up another machine.

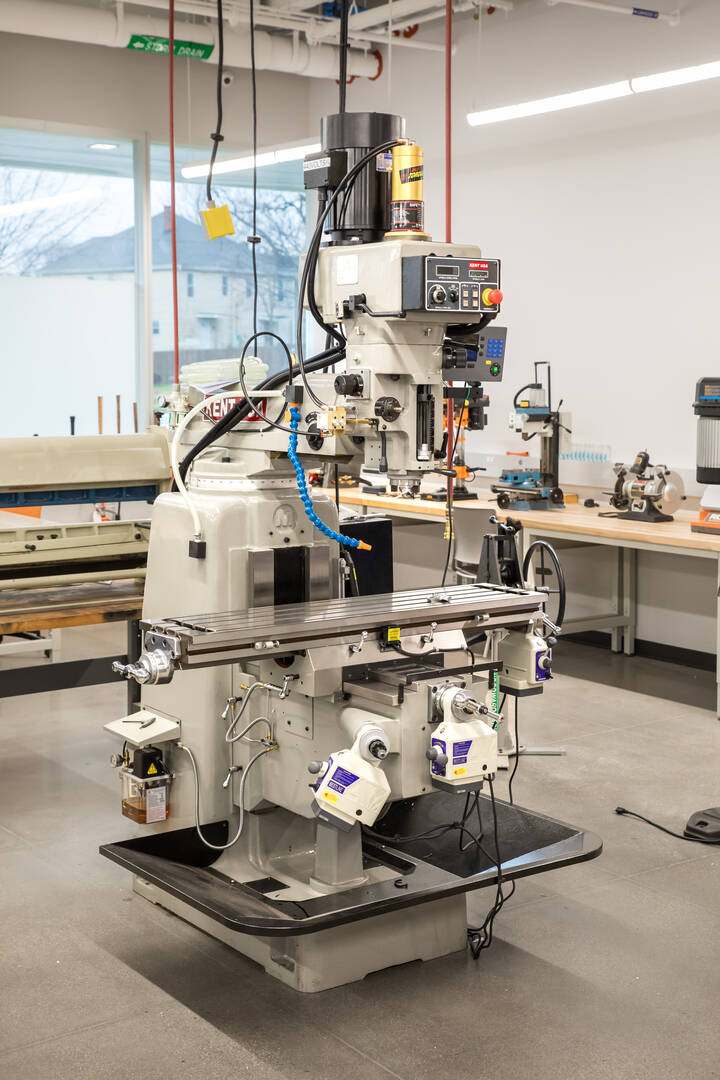
Kent Manual Mill
This large milling machine is capable of producing very large and complex products, depending on the user’s skill set. As a manual machine, the student operator will have full control on how it moves in each of its axes and can adjust feed rates as needed. Similar to the combo lathe, this machine comes with an optional 4th axis turning attachment to make even more complex parts.

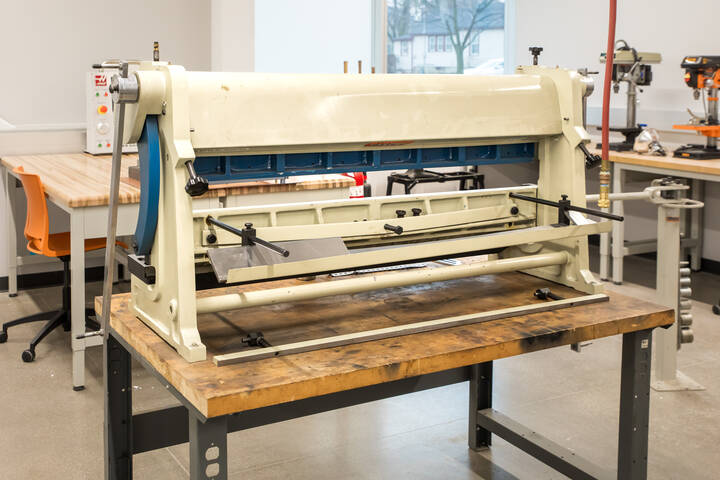
Baileigh 3 in 1 Machine
This versatile tool is used to shape metal materials into products. For instance, students can make a circular fire pit by using the machine’s sheet metal roller. The binding function can compress metal parts to have specific angles at the joints, Finally, it possesses a large sheer designed to cut sheets of metal.

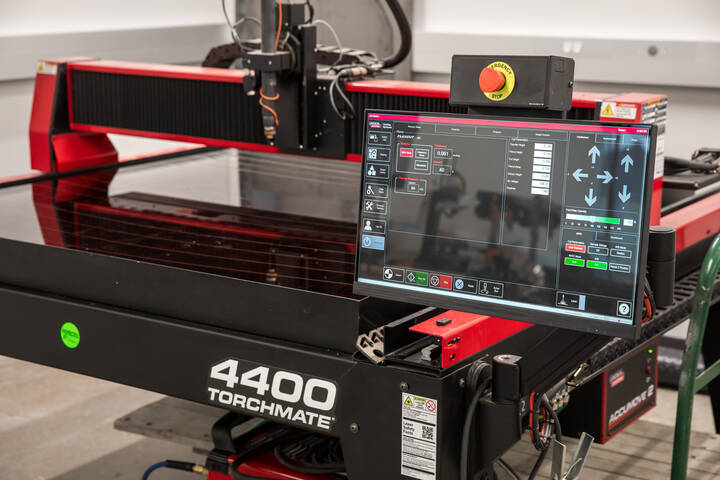
Plasma Table
This CNC plasma table functions like a laser engraver. The material is fixed in place while the machine blasts plasma onto to replicate the shape/design made by the student. This machine can cut through material from the thickness of regular sheet metal to a few inches thick.

HAAS CNC Lathe
After learning how to use a manual lathe to make a part, students learn how to replicate the same part on this CNC machine. To do so, students use CAD and CAM software programs to draw the part. The finished drawing is output into G-code—coding that instructs the machine what to do to replicate the part. This experience is particularly beneficial for mechanical engineering technology students.
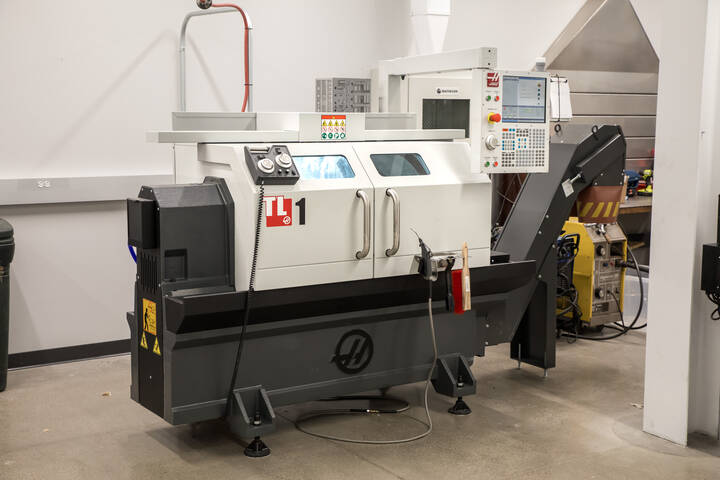

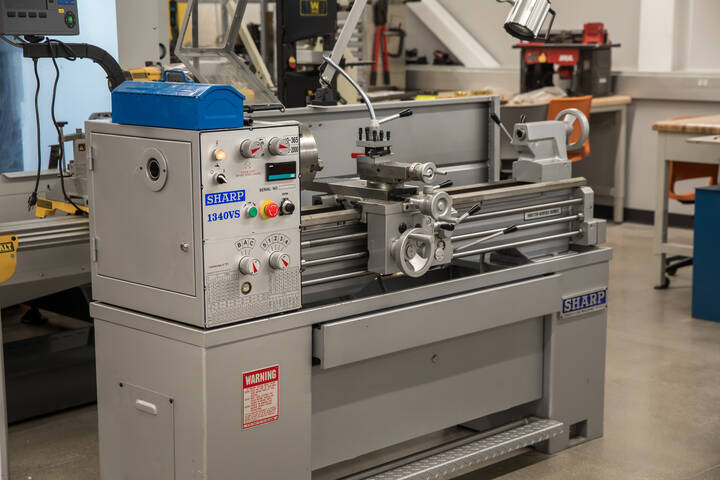
Sharp Manual Lathe
This machine allows student to make products that are circular in nature such as shafts, bolts, doorknobs, etc. It does this by rotating the stock material while the user manually controls the position of the cutting tool. Stock is removed until the desired shape and size is achieved.

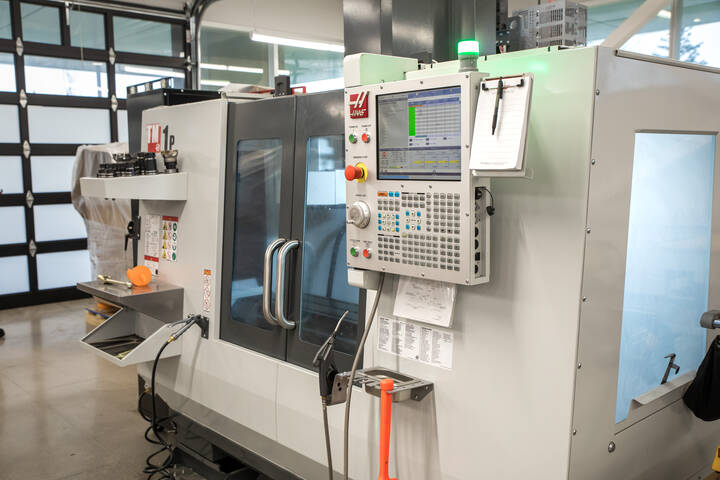
HAAS CNC Mill
Because of its functional versatility of this machine, students are able to:
- Experiment with different ways to fix material to a machine bed so it can’t move during production
- Familiarize themselves with different cutting tools and the results they produce on different materials
- Use CAD/CAM software programs to create G-code that enables the machine to produce parts with high accuracy and efficient repeatability
Experiences gained from this machine are particularly beneficial for mechanical engineering technology students.

This lab is utilized by students of any engineering major to 3D print parts as required by various classwork and to enhance their understanding of product development. It is essentially a makerspace for 3D printing but also contains various hand tools and consumables for making products in other mediums.
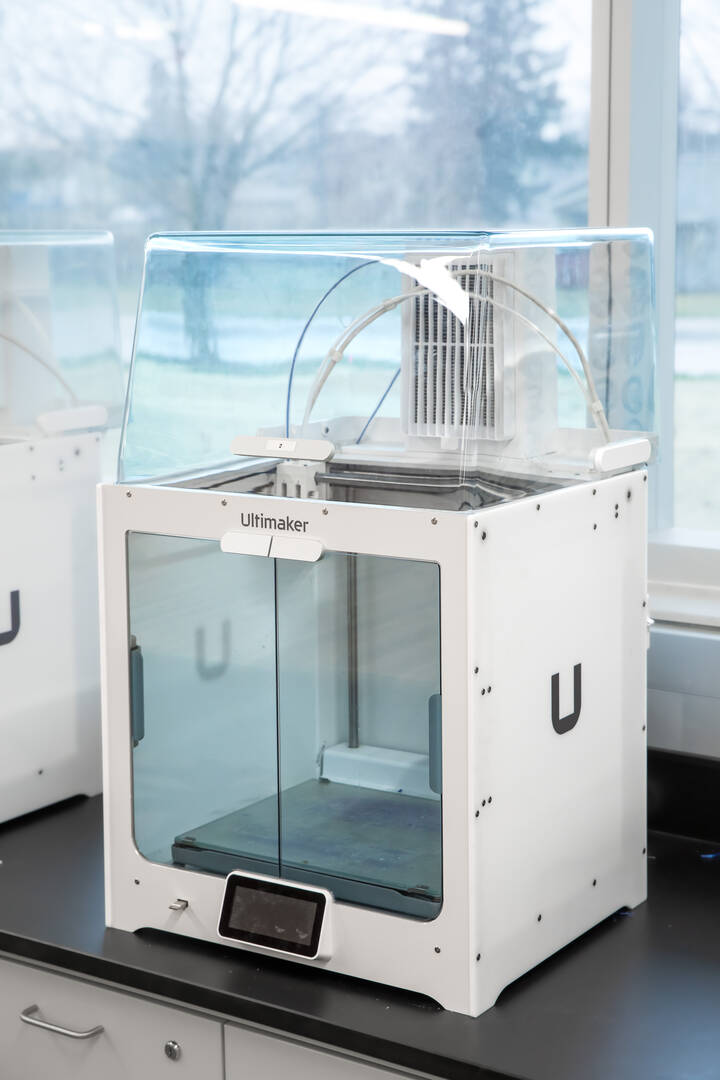
Ultimaker S5
These 3D printers are used frequently by our biomedical and mechanical engineering students. Versatile and compatible with a wide variety of materials, these printers are used to help fabricate different models and devices that are used for experiments in other labs.
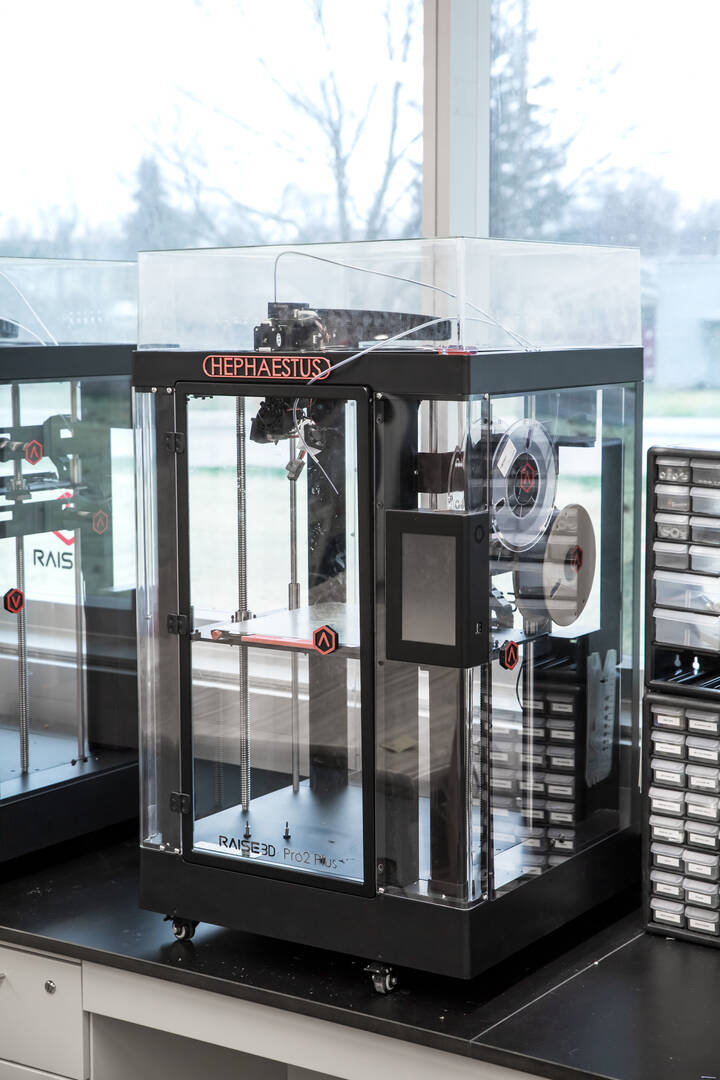
Raise3D Pritner
These 3D printers are used by students who design models that require more advanced fabrication capabilities. In addition, these machines are used to teach students how to repair 3D devices and understand how different settings can impact the fabrication process.

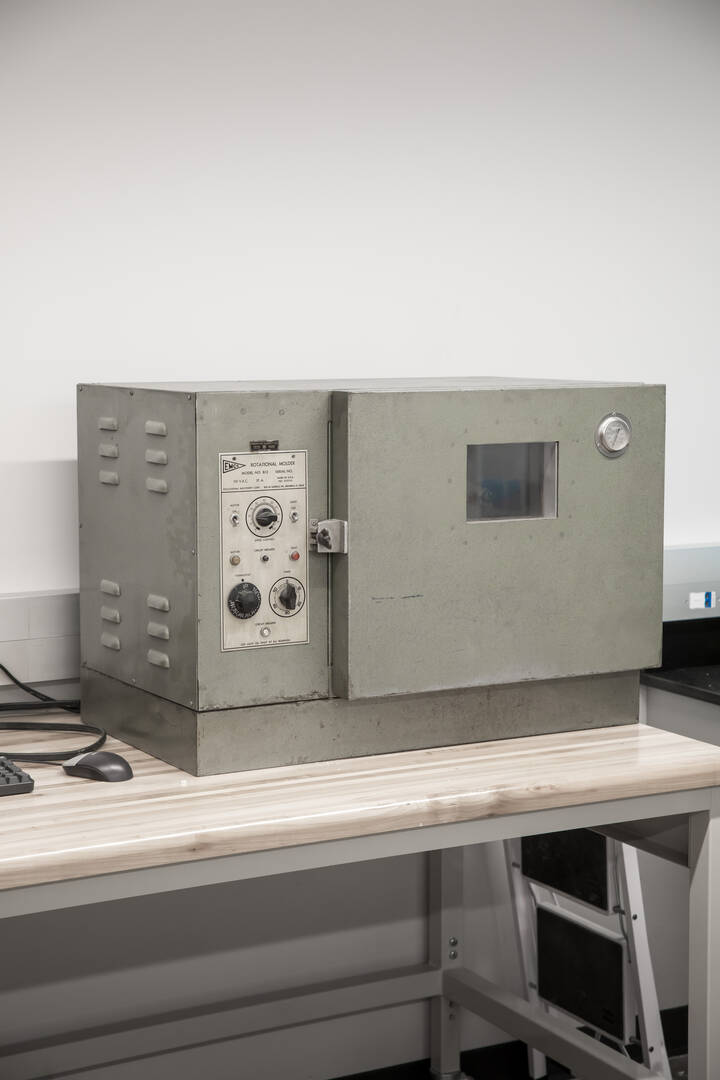
EMCO Rotary Molder
This device is used to fabricate hollow plastic products from molds machined on a CNC turning center. The system helps students learn that some products can only be manufactured when multiple machines are used.

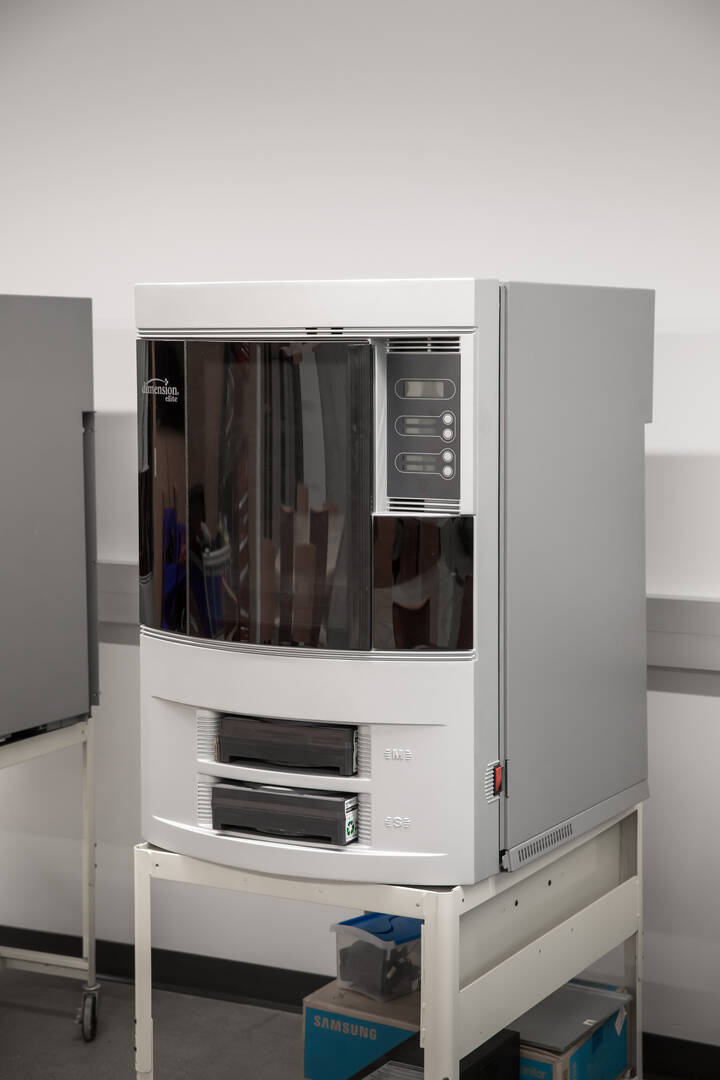
Stratasys Dimension Elite
These are industrial-grade 3D printers that show students how additive machines designed for manufacturing differ from ones developed for commercial use. These machines are capable of fabricating prototypes with exquisite detail.

This fully configured teaching laboratory is equipped with Windows 64-bit workstations, which support virtual machines and contain the latest version of industry-standard software for:
- Application development
- Web and mobile application development
- Database design and implementation
- Networking technologies
- Operating systems
- Computer security and information assurance
Students can also access this lab during non-teaching hours to complete assignments and research.
From state-of-the art machines like collaborative robots to legacy equipment that facilitated the development of current technology, students will have access to the widest range of automation applications in the region.
Featured Equipment:
- APT Connected Smart Manufacturing System – 4 Robot Cell
- Universal Robots Robotic Arm, UR3 – 6-axis
- Denso Robotic Arm, VP-6242G – 6-axis
- Mitsubishi Robotic Arm, RV-M2 – 5-axis
- Intelitek Robotic Arm, ER4U – 5-axis
- CNC Jr. CNC Milling Machine
- Intelitek CNC Turning Center
- Allen-Bradley Traffic Lights Simulator
Students will experiment with the mechanical properties of solid materials.
Featured Equipment:
- Advanced structures set
- Abrasimet 2 abrasive cutter
- Simplimet 2 mounting press
- Nano 2000T grinder/polisher
- Tensile/Compression tester
- Hardness tester
- Statics torsion package
- IZOD impact tester
- Beam apparatus
- HiTorque mini mill
- 10-inch drill press with laser
- Force table
- Statics board
- Ballistic pendulum
- Microscope
- Shaker table
- Vibration test trainer
Students learn to wire and build their own networks here. The technology will also allow them to simulate larger-scale networks, and examine network vulnerabilities and how to protect against them.
Equipped with three Amatrol trainers, which are composed of an Allen-Bradley AB5300 L16 processor, a fault insertion system, and a PanelView Plus compact HMI panel, this lab will give students the opportunity to mimick practical industrial temperature control applications, variable speed drive applications, reversing contactor applications and stepper motor control applications.
Located in the Zollner Engineering Center Room Z152, students perform various experiments and test physical principles that help reinforce what they learn in in a variety of physics courses. They will explore the fundamental aspects of mechanics including kinematics, Newton’s Laws, work and energy, rotational motion, simple harmonic motion and wave motion, as well as electromagnetic concepts.
Students will have access to various types of state-of-the-art, computer-interfaced AC and DC motors, and single- and three-phase transformers. Using a servo drive and braking system, it is possible to easily simulate the performance of various motors (e.g., fans, pumps, compressors, flywheels) under different industrial loads.
Students will work with robots used in manufacturing processes and other job applications. Some of these job-application robots will include tile runners, which are similar to those used by police forces and NASA.
Featured Equipment:
- Amatrol Smart Factory Industry 4.0 8 Station assembly line
- Amatrol Tabletop Mechatronics Learning System Industry 4.0
This lab was created to be a collaborative project-based learning space for software engineering majors. It houses few university computing resources. Instead, it was created with a modular design to improve seating, power and network access. This design allows various classes to go through the Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC) in a simulated work environment with ad hoc teams using agile and scrum methodologies.
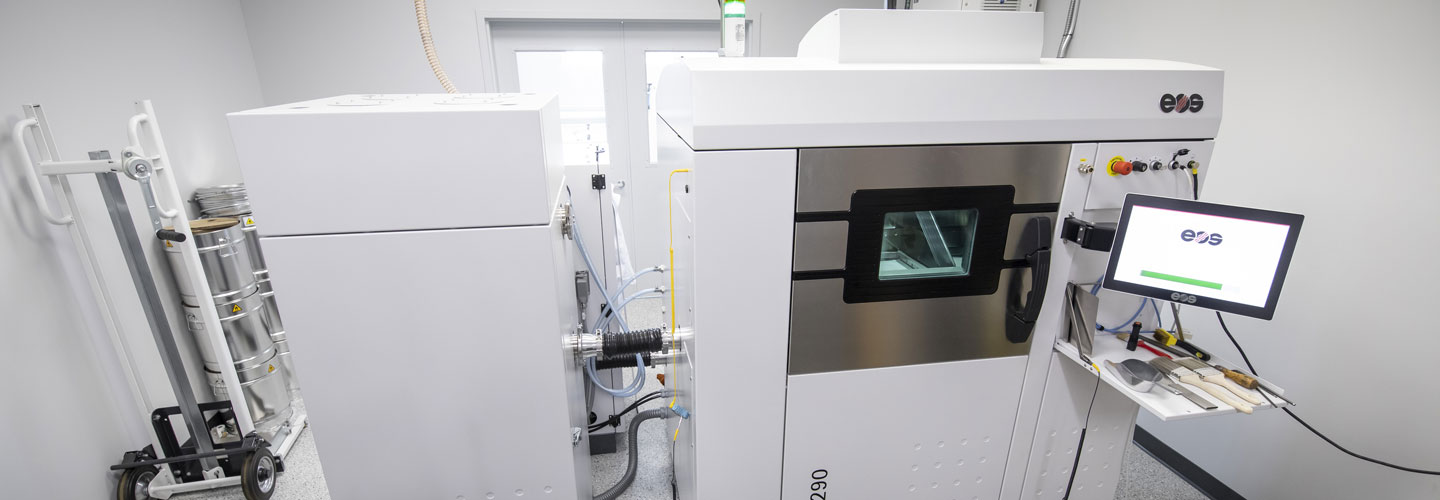
Students will use hydraulic and pneumatic equipment to explore fluid mechanics, heat transfer, HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) and energy systems. In addition, this lab is home to the EOS M 290 Metal 3D Printer, on which students will learn about the direct laser sintering metal (DLSM) process.
Featured Equipment:
- Hydraulic/Pneumatic trainer
- Digital hydraulic bench
- Hydrostatic experiment
- Losses in piping systems laboratory
- Mass hydraulic bench
- Steam turbine experiment
- Two-stage pumps
- Heat conduction experiment
- Heat exchanger service module
- Cooling tower experiment
- Wind tunnel
- Internal combustion engine test bench
Temperature Measurement and Calibration
Students learn how to measure temperatures in different units using various types of temperature sensors. They also learn how to calibrate commonly used temperature sensors, which reveal the important relationship between data quality and instrument calibration.

Saturation Temperature and Pressure
Students learn about the relationship between pressure and the temperature of water, how pressure affects boiling point and how much vapor content exists in a mixture of liquid and vapor.

Thermal Radiation
Students study the laws of heat transfer by radiation through various finishes of the same material. Students also investigate the relationship between radiation and temperature.

Natural and Force Convection
Students study the properties of and the differences between heat transfer caused by natural convection (which does not require the mechanical movement of a liquid or a gas) and forced convection (which requires the mechanical movement of a liquid or a gas). Students also examine different extended surfaces designed to improve heat transfer by convection.

Heat Transfer by Conduction
Students investigate the properties of heat transfer by conduction by studying the thermal conductivity of various materials. Different types of coordinate systems can be used for various material geometry.

Geothermal Trainer
This system teaches students how to harvest geothermal energy for heating and cooling.

Miniature Power Plant
This steam power plant model is equipped with a boiler system, a steam turbine, a pump, and condenser, giving students an opportunity to monitor and control the plant operation and its performance.

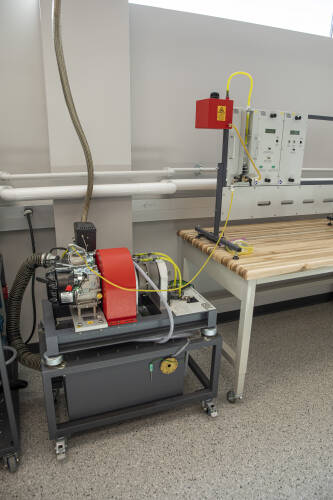
Four-Stroke Internal Combustion Engine
Students learn the inner workings of the most common internal combustion engine designed for motorized land transport. They are used in automobiles, trucks, diesel trains and motorcycles.
Flow Measurement
With this equipment, students will use typical methods to measure the flow of water and will study the relationship between rate of flow and velocity.
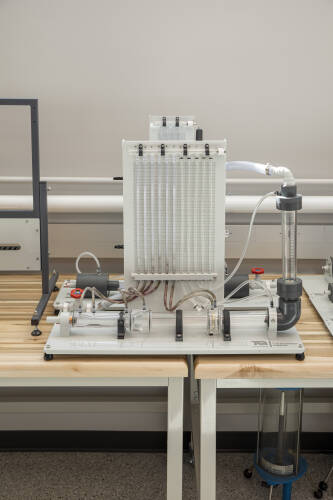
Heat Exchanger
Students investigate the performance of different types of heat exchangers used in many industrial applications, such as air conditioning.

Centrifugal Pump
Students study the performance operating centrifugal pumps, which are the most popular and commonly used type of pump for the transfer of fluids.

Center of Pressure
This equipment will help students determine the static force exerted by a fluid on a submerged surface, similar to how a hydraulic dam is influenced by water.

Vapor Compression Refridgeration Cycle
Comprised of a compressor, a condenser, an expansion valve/throttle valve and an evaporator, this equipment teaches students how a refrigerator or a window air conditioning unit works.

Cooling Tower
Students learn about this essential part of a power plant, which removes heat by spraying water down through the tower to exchange heat with the surrounding air. The cooled water returns back to the power plant for continuous operation.

Fuel Cell Trainer
With this equipment, students learn what comprises a fuel cell and how they work.

Photovoltaic Troubleshooting Station
Students learn a range of solar photovoltaic (PV) operation, maintenance and troubleshooting skills through hands-on experience with real industrial solar PV components.

Wind Tunnel
Students learn about the aerodynamics of vehicles and flying objects with this equipment, which includes a smoke generator to help with visualization.

Hydraulic Trainer
Students learn how pneumatic and hydraulic components affect the functions of machines and devices that operate based on hydraulic pressure.


